Unit 05 - Raster processing¶
Raster data processing is always limited to the current computational region.
Let’s demostrate raster processing on map algebra based
computation of NDVI (Normalized difference vegetation
index). The key GRASS tool that allows a user to do the map algebra
is r.mapcalc. A GUI tool for map algebra can be launched
from or by
 Raster map calculator from the main
toolbar.
Raster map calculator from the main
toolbar.
To compute NDVI, the red (VIS) and near-infrared (NIR) bands are
required. In the case of Sentinel-2, it refers to 4th and 8th
band. Missing Sentinel-2 8th band can be imported as explained in
Unit 03 - Data Management from L2A_T32UPB_20170706T102021_B08_10m.jp2 file.
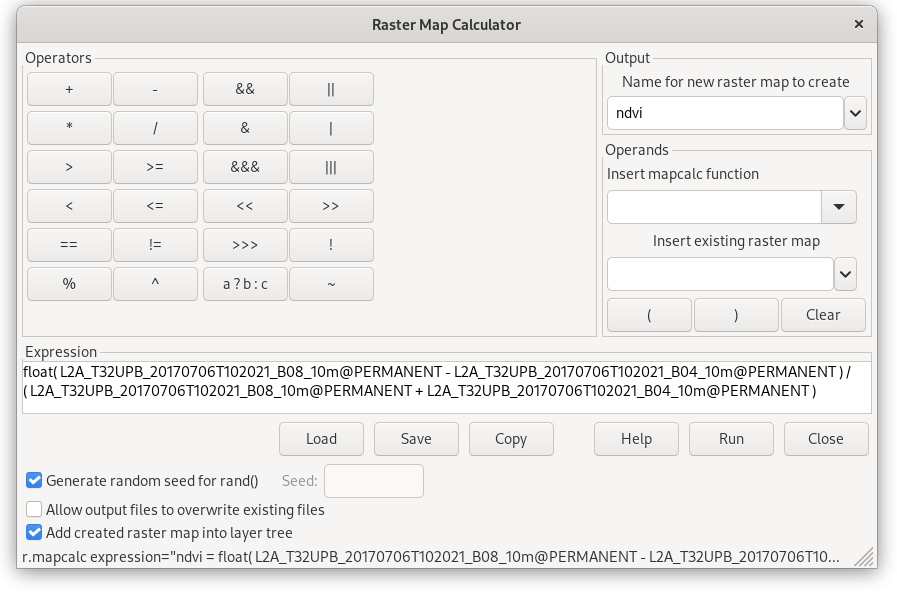
Fig. 35 GUI map algebra tool. Compute NDVI by Expression. Result of computation is defined by Output section.¶
Corresponding command (map names shorten):
r.mapcalc expression="ndvi = float(B08_10m - B04_10m) / ( B08_10m + B04_10m )"
Note
Because all input raster maps are CELL type (integer) at
least one sub-result must be converted to floating-point by
float() function. Otherwise result would be also CELL
map (integer: -1, 0, 1).
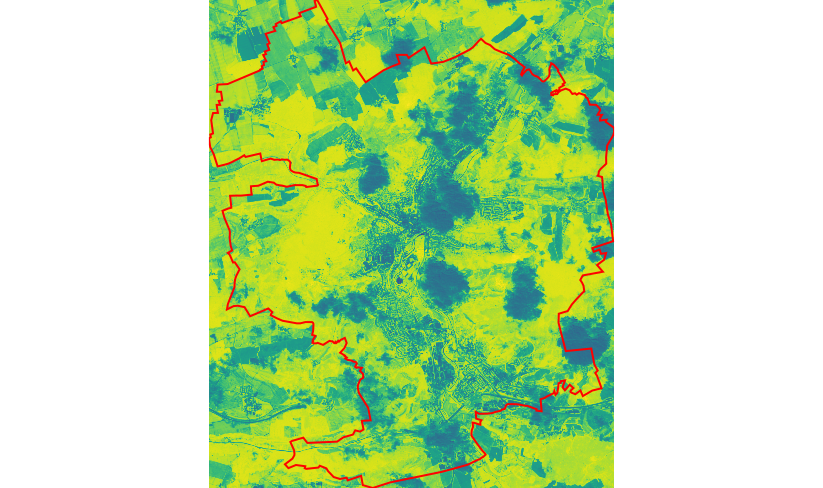
Fig. 36 NDVI computed by r.mapcalc map algebra tool (Jena city in red color).¶
Result requires some improvements:
default color table viridis is not suitable for NDVI values
NDVI was computed also in cloudy areas
The first shortcoming can be easily solved by changing color table to
ndvi as described in Color table section. The second requires
setting a mask to ignore cloudy areas by the computation. Raster mask
can be created by r.mask. Like other tools from the
r.* family, it operates in the current computational region.
Mask¶
Let’s create raster mask from cloud mask vector map in inverse manner.
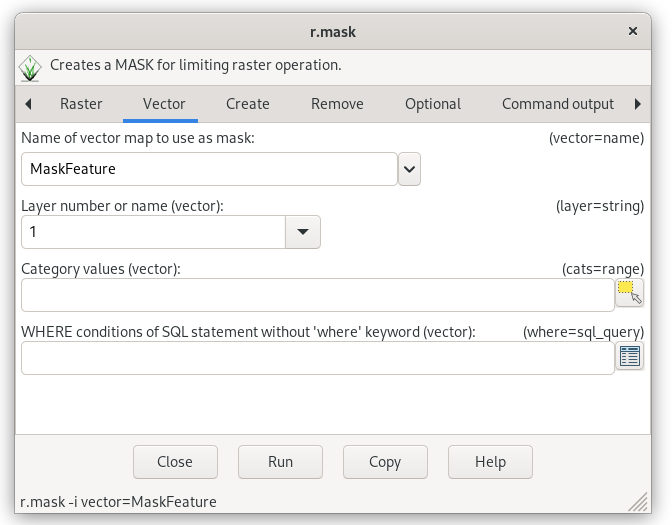
Fig. 37 Creating raster mask from an input vector map.¶
r.mask -i vector=MaskFeature
Important
The mask is used globally in the given mapset for each subsequent calculation operation until it is deleted.
Note
Cloud mask provided by Sentinel products is not perfect, but it is a good starting point for us.
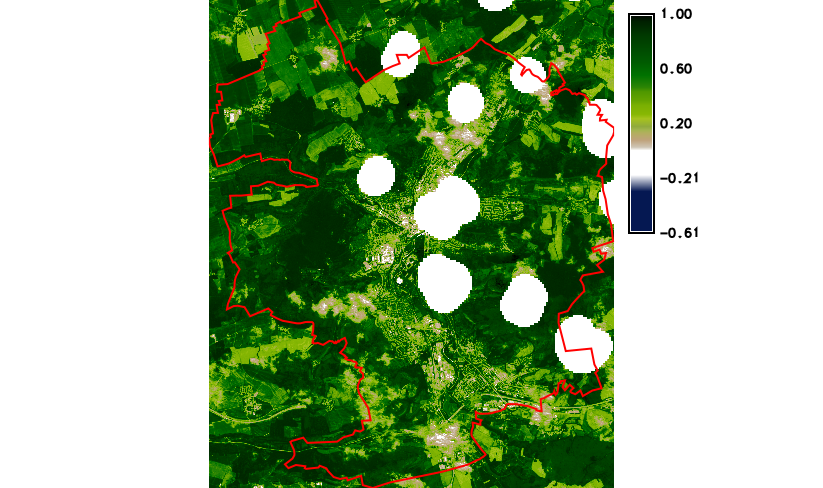
Fig. 38 Final NDVI result with cloud mask and simple legend added to map
display by  Add map elements (Add raster
legend) from Map Display toolbar.¶
Add map elements (Add raster
legend) from Map Display toolbar.¶
A mask can be deactivated r.mask -r command.
Recommended approach for computing NDVI¶
Note that there is specialized tool for computing various vegetation indices including NDVI - i.vi. This tool makes NDVI computing even simpler.
Let’s recompute ndvi map using i.vi (map names shorten):
i.vi red=B04_10m output=ndvi viname=ndvi nir=B08_10m