Unit 17 - DTM script parallelization¶
This unit is focused on computing parallelization. Sample script below produces seamless DTM (Digital Terrain Model, see Unit 16 - Lidar, DTM interpolation) from bunch of LAS/LAZ files. Computation will be split into tiles and performed in parallel.
DTM interpolation in parallel¶
User interface contains two major parameters, directory (line 6) for input directory with input LAS/LAZ files, and elevation (line 9) name for output elevation raster map mosaics. The resolution of output DTM is defined by resolution parameter (line 13). And finally number of processes running in parallel will be controlled by nproc (line 18) parameter.
A script consists of three main functions:
1. import_files() to import input LAS/LAZ files (line
33). Import process can be done in parallel by
ParallelModuleQueue from PyGRASS library (see
Unit 11 - PyGRASS scripting for PyGRASS intoruction), lines 37, 42, 57-58, 60.
2. create_dtm_tiles() to compute DTM per tile (line 67)
using v.surf.rst. DTM tiles need to be computed with a
reasonable overlap in order to create seamless mosaics, see
73-76. Tiles can be processed in parallel too, see
nproc option on line 82.
3. patch_tiles() to patch DTM tiles together by
r.series, see 86. From overlapping cell values is
computed an average value. This is main reason why r.patch
is not used here.
1#!/usr/bin/env python
2
3#%module
4#% description: Creates DTM from input LAS tiles.
5#%end
6#%option G_OPT_M_DIR
7#% required: yes
8#%end
9#%option G_OPT_R_ELEV
10#% description: Name for output elevation raster map mosaics
11#%end
12#%option
13#% key: resolution
14#% description: Output resolution
15#% type: double
16#%end
17#%option
18#% key: nprocs
19#% description: Number of processes per tile
20#% answer: 1
21#% type: integer
22#%end
23
24import os
25import sys
26import time
27from copy import deepcopy
28
29import grass.script as gs
30
31from grass.pygrass.modules import Module, ParallelModuleQueue
32
33def import_files(directory):
34 start = time.time()
35
36 # queue for parallel jobs
37 queue = ParallelModuleQueue(int(options['nprocs']))
38
39 import_module = Module('v.in.lidar',
40 flags='otb',
41 overwrite=True,
42 run_=False
43 )
44
45 maps = []
46 for f in os.listdir(directory):
47 if os.path.splitext(f)[1] != '.laz':
48 continue
49 fullname = os.path.join(directory, f)
50 basename = os.path.basename(f)
51 # '-' is not valid for vector map names
52 # vector map names cannot start with number
53 mapname = "las_{}".format(os.path.splitext(basename)[0].replace('-', '_'))
54
55 maps.append(mapname)
56 gs.message("Importing <{}>...".format(fullname))
57 import_task = deepcopy(import_module)
58 queue.put(import_task(input=fullname, output=mapname))
59
60 queue.wait()
61
62 if not maps:
63 gs.fatal("No input files found")
64
65 return maps
66
67def create_dtm_tiles(maps, res, nprocs, offset_multiplier=10):
68 offset=res * offset_multiplier
69
70 for mapname in maps:
71 Module('g.region',
72 vector=mapname,
73 n='n+{}'.format(offset),
74 s='s-{}'.format(offset),
75 e='e+{}'.format(offset),
76 w='w-{}'.format(offset)
77 )
78
79 Module('v.surf.rst',
80 input=mapname,
81 elevation=mapname,
82 nprocs=nprocs,
83 overwrite=True
84 )
85
86def patch_tiles(maps, output, resolution):
87 gs.message("Patching tiles <{}>...".format(','.join(maps)))
88 Module('g.region', raster=maps, res=resolution)
89 Module('r.series', input=maps, output=output, method='average', overwrite=True)
90 Module('r.colors', map=output, color='elevation')
91
92def main():
93 start = time.time()
94
95 maps = import_files(options['input'])
96 create_dtm_tiles(maps,
97 float(options['resolution']),
98 int(options['nprocs'])
99 )
100 patch_tiles(maps,
101 options['elevation'],
102 options['resolution']
103 )
104
105 gs.message("Done in {:.0f} min".format((time.time() - start) / 60.))
106
107 return 0
108
109if __name__ == "__main__":
110 options, flags = gs.parser()
111
112 sys.exit(main())
Sample script to download: create-dtm.py
Note
The script is taking a long time with all the tiles from
/home/geodata/lidar/laz directory. Choose few tiles
for testing.
Create a new directory eg. /tmp/lidar and link some (2
or 3) of the LAZ files with
ln -s /home/geodata/lidar/laz/32-1-514-136-15.laz /tmp/lidar/
Use /tmp/lidar as input in the create-dtm.py script
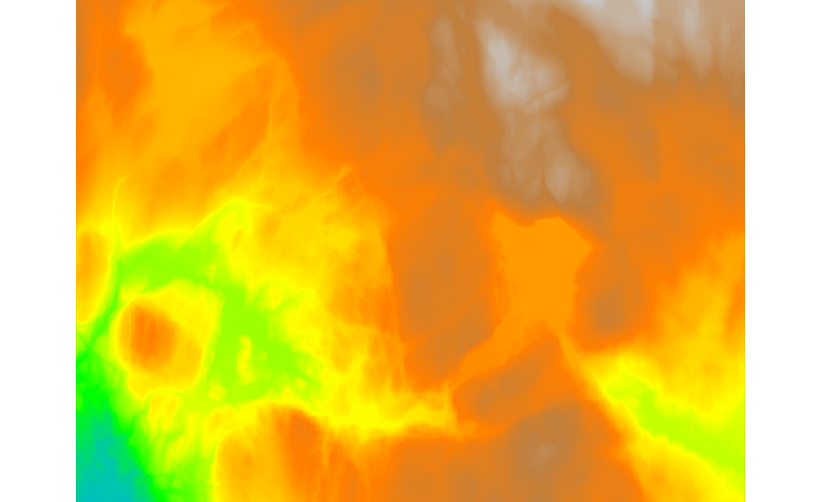
Fig. 100 DTM created from all available tiles.¶
DTM comparision¶
In this session we are going to calculate the Canopy Height Model (CHM), it is the difference between interpolated DSM and imported EUDEM DTM
The CHM is computed using r.mapcalc, executing the difference between DSM and DTM
r.mapcalc expression="chm = DTM_laz - dem"
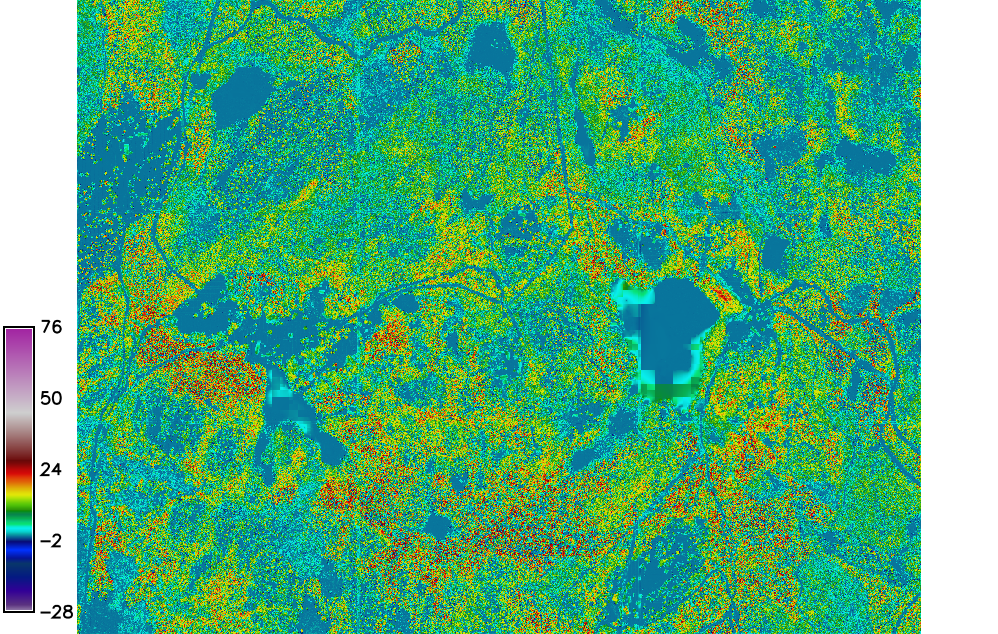
Fig. 101 The CHM map.¶
Tip
To have better CHM it is possible to download DTM files from hoydedata.no. You can import all TIF files using checking Directory as Source type and selecting the directory where the TIF files are.
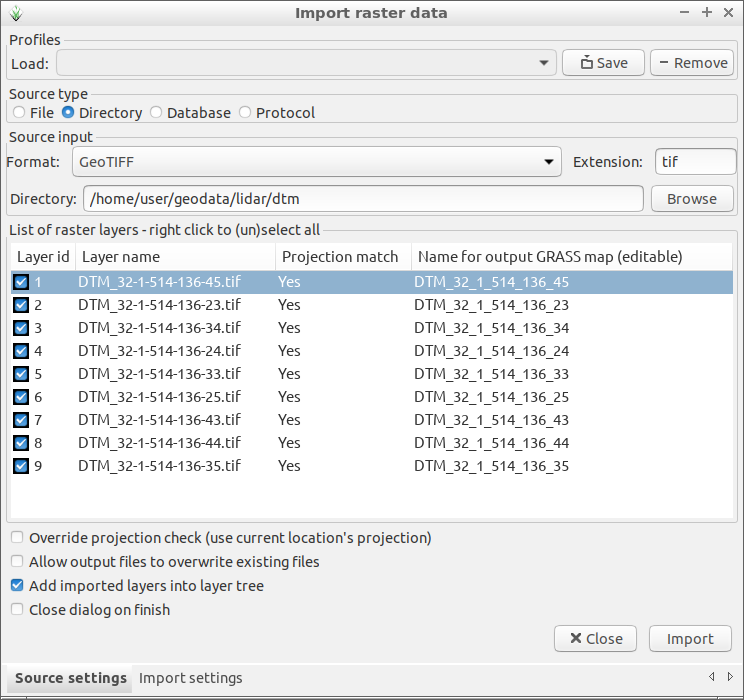
Fig. 102 Import all DTM TIF files from for exampe geodata/lidar/dtm/
directory.¶
Once DTM tiles are imported you can patch them using r.series and set the color to elevation by r.colors.
r.series input=`g.list type=raster pattern=DTM_* sep=','` output=DTM_patch
r.colors map=DTM_patch color=elevation

Fig. 103 Patched DTM.¶
Now it is possible to run the previous r.mapcalc command changing dem with DTM_patch